Understanding Dopamine: What It Is and Why It Matters
Dopamine is often called the brain's 'feel-good' chemical, but it's so much more than just that. This neurotransmitter helps control your mood, motivation, focus, and even how you experience pleasure. When dopamine levels are just right, you feel motivated and happy. But when they dip or spike, it can affect mental health and behavior.
So, what exactly does dopamine do? It acts like a messenger between nerve cells in your brain, influencing many processes like movement, reward, and learning. This means dopamine is key for habits, decision-making, and how you respond to rewards and challenges.
Signs You Might Have Dopamine Imbalance
Noticing changes in your energy, mood swings, or difficulty concentrating? These could be hints that your dopamine is off. Low dopamine levels might make you feel tired, less motivated, or even depressed. On the flip side, too much of it can lead to feelings of anxiety or impulsive behaviors.
Some medical conditions, like Parkinson’s disease, show how critical dopamine balance is. In Parkinson’s, dopamine-producing cells are damaged, leading to movement problems. Treatments often aim to restore dopamine levels to help manage symptoms.
Keeping Dopamine in Check: What You Can Do
Luckily, there are ways you can support healthy dopamine levels naturally. Regular exercise is a top booster—it doesn’t have to be intense; even daily walks can help. Eating foods rich in tyrosine, an amino acid building block for dopamine, like almonds, bananas, and eggs, is another simple step.
Mindful activities such as meditation or hobbies that you enjoy also give your dopamine system a positive nudge. But be careful with habits that flood dopamine unnaturally, like excessive social media or substance use—they might feel rewarding at first but can cause long-term imbalances.
Understanding how dopamine works in your body can help you take charge of your mood, motivation, and overall brain health. If you think dopamine-related issues might be affecting you, talking to a healthcare provider is always a smart move—they can guide you safely on treatments or lifestyle changes.
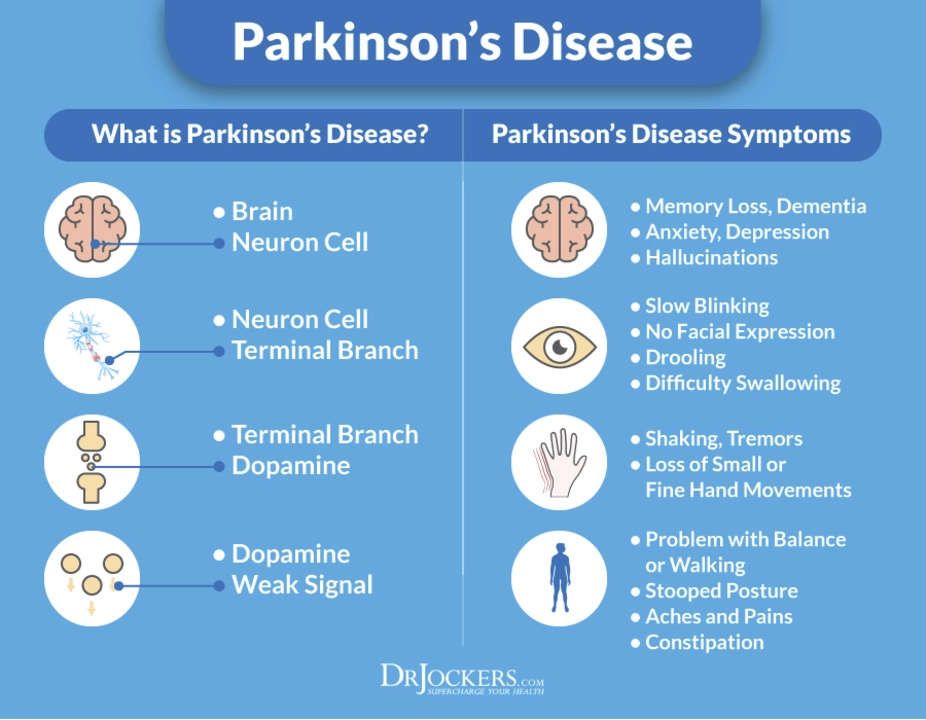
Understanding the Role of Dopamine in Parkinson's Disease
In my recent exploration of Parkinson's Disease, I've discovered the crucial role dopamine plays in this neurological disorder. Dopamine, a vital chemical messenger in our brains, is significantly reduced in Parkinson's patients, leading to issues with movement and coordination. This decrease in dopamine is primarily caused by the death of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. Understanding the role of dopamine in Parkinson's Disease is essential for developing effective treatments and therapies. Further research on this topic may help improve the lives of those affected by this debilitating condition.