Archive: 2023/05 - Page 2

Budesonide and its potential role in treating COVID-19
I recently came across some interesting information about Budesonide, an anti-inflammatory drug, and its potential role in treating COVID-19. Budesonide is commonly used to treat asthma and other respiratory conditions. It has been suggested that this drug could help reduce inflammation caused by the virus, leading to faster recovery times for patients. Clinical trials are currently underway to determine the effectiveness of Budesonide in treating COVID-19. I'm eager to see the results and will definitely keep you all updated on any developments in this promising area of research.
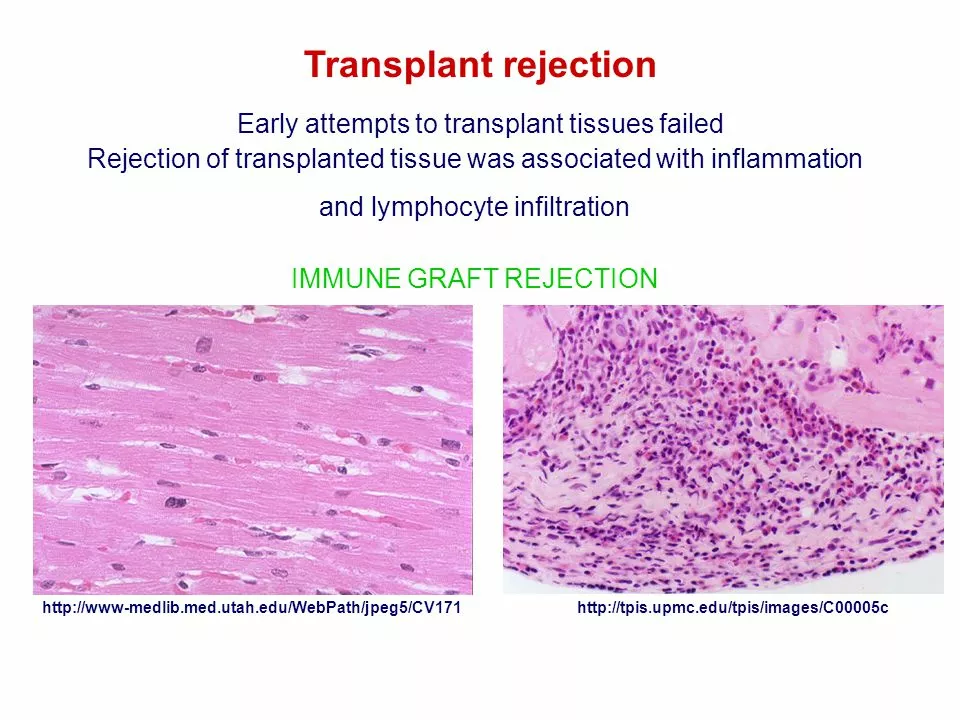
Organ Rejection and Ethnicity: The Impact of Genetic Factors
In my recent research, I've come across the fascinating topic of organ rejection and ethnicity, specifically focusing on the impact of genetic factors. It's intriguing to see how genetic variations among different ethnic groups can affect organ transplant outcomes. For instance, certain populations may experience higher rates of organ rejection due to a lack of well-matched donors within their ethnic group. This highlights the importance of increasing organ donor awareness and participation among diverse populations to ensure the best possible outcomes for all patients in need of transplants. Overall, understanding the role of genetic factors in organ rejection is crucial for improving transplantation success rates and saving more lives.
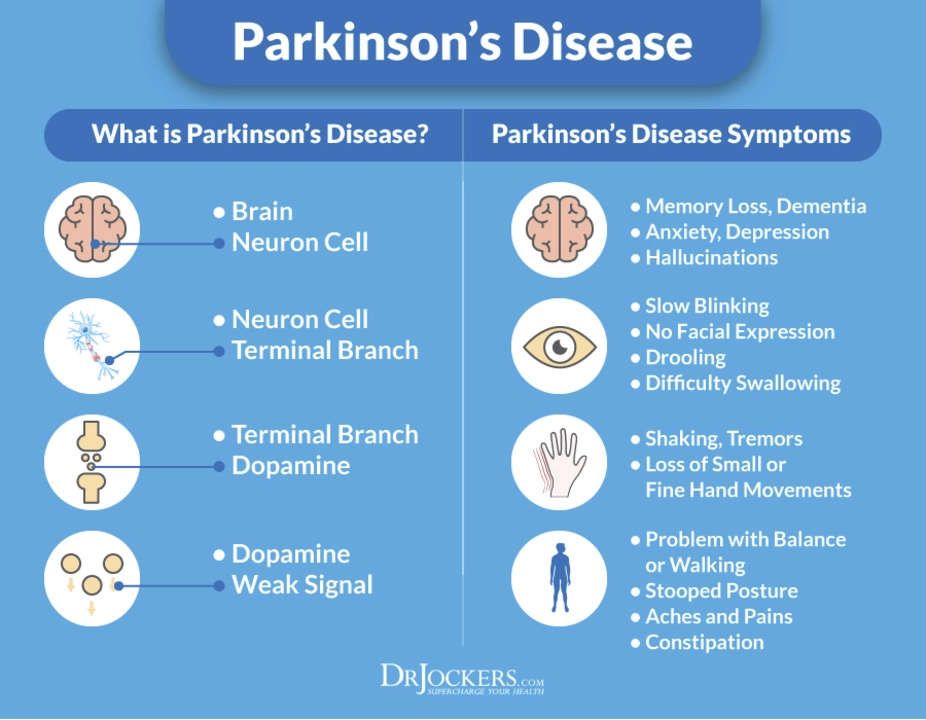
Understanding the Role of Dopamine in Parkinson's Disease
In my recent exploration of Parkinson's Disease, I've discovered the crucial role dopamine plays in this neurological disorder. Dopamine, a vital chemical messenger in our brains, is significantly reduced in Parkinson's patients, leading to issues with movement and coordination. This decrease in dopamine is primarily caused by the death of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. Understanding the role of dopamine in Parkinson's Disease is essential for developing effective treatments and therapies. Further research on this topic may help improve the lives of those affected by this debilitating condition.