Understanding Organ Rejection and Ethnicity
Organ rejection is a common issue that many transplant recipients face. While various factors can contribute to the rejection of a transplanted organ, one aspect that is often overlooked is the role of ethnicity and genetic factors in this process. In this article, we will explore the impact of genetic factors on organ rejection and how it relates to different ethnicities. We will discuss several factors that contribute to organ rejection, including genetic compatibility, immune response, and access to transplantation.
Genetic Compatibility and Organ Transplant Success
One of the main factors that influence the success of an organ transplant procedure is genetic compatibility between the donor and the recipient. The more similar the genetic makeup of the donor and recipient, the higher the chances of the transplant being successful. This is because the recipient's immune system is less likely to recognize the transplanted organ as foreign and attack it.
Genetic compatibility is determined by the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system, which plays a significant role in the immune response. HLA matching is crucial in organ transplantation, and the closer the match, the lower the risk of organ rejection. Studies have shown that the success rate of organ transplants increases when the donor and recipient share the same ethnicity, as they are more likely to have similar HLA types.
Impact of Ethnicity on Immune Response
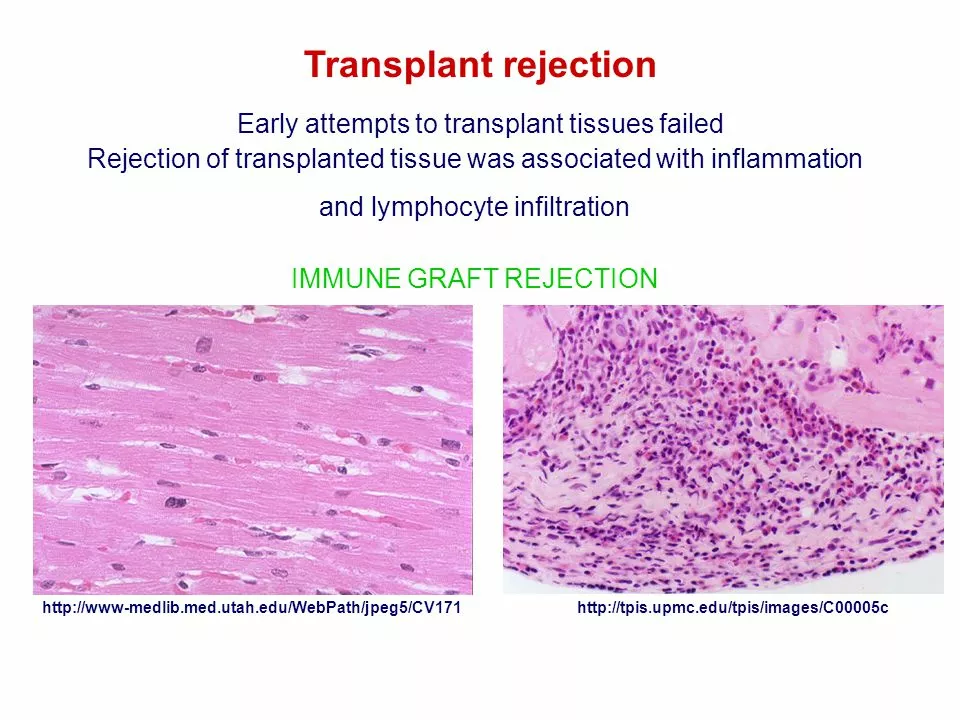
As mentioned earlier, the HLA system plays a crucial role in the immune response. Different ethnic groups have different HLA types, which can affect the immune response and the likelihood of organ rejection. It has been observed that some ethnic groups have a higher risk of organ rejection due to genetic differences in their immune systems.
For example, African Americans have been found to have a higher risk of organ rejection compared to Caucasians. This is partly because African Americans have a more diverse HLA system, making it more difficult to find a compatible donor. Additionally, some studies suggest that African Americans may have a stronger immune response, which can lead to a higher rate of organ rejection.
Organ Transplant Access and Ethnicity
Another factor that can impact organ rejection rates is access to transplantation. Ethnic minorities often have lower rates of organ donation and are less likely to receive transplants compared to the majority population. This can lead to longer waiting times for a compatible organ, which can have detrimental effects on the recipient's health and increase the risk of organ rejection.
Furthermore, disparities in healthcare access and quality can also contribute to higher organ rejection rates among ethnic minorities. Lower quality healthcare can result in inadequate monitoring and management of organ transplant recipients, increasing the risk of organ rejection.
Improving Organ Transplant Outcomes for All Ethnicities
To address the issue of organ rejection and ethnicity, it is essential to increase awareness about organ donation and transplantation within diverse communities. This can help promote organ donation among ethnic minorities and improve access to transplantation for these groups.
Additionally, healthcare providers should be educated on the importance of HLA matching and the impact of ethnicity on organ transplantation outcomes. This can help ensure that transplant recipients receive the best possible care and reduce the risk of organ rejection.
Technological Advances in Organ Transplantation
With advancements in technology and medical research, new methods are being developed to improve the success rate of organ transplants. One such approach is the use of stem cells to create personalized organs that are genetically compatible with the recipient. This can significantly reduce the risk of organ rejection and improve transplantation outcomes for all ethnicities.
Furthermore, advancements in immunosuppressive medications are also helping to reduce the risk of organ rejection. These medications help to regulate the recipient's immune response and prevent the attack on the transplanted organ.
Conclusion
In conclusion, organ rejection and ethnicity are closely linked, with genetic factors playing a significant role in this relationship. By increasing awareness about organ donation and improving access to transplantation for diverse communities, we can help reduce disparities in organ transplant outcomes. Additionally, continued research and technological advancements can help improve the success rate of organ transplants for all ethnicities, ultimately saving more lives.
Yassin Hammachi
May 5, 2023 AT 23:05Organ transplantation is already a marvel of modern medicine, but the hidden layers of genetic compatibility add a whole new dimension to the conversation.
When we talk about HLA matching, we aren't just swapping tissues; we're aligning two intricate immune histories that have evolved over millennia.
This alignment often mirrors the subtle genetic signatures that differ across ethnic groups, which is why donors and recipients from the same background tend to have a smoother ride.
Yet, the science does not exist in a vacuum; socioeconomic factors shape who gets on the waiting list and who gets the organ in the first place.
Communities that have historically been marginalized also tend to have fewer registered donors, creating a feedback loop of scarcity.
From a philosophical standpoint, this raises questions about fairness and the collective responsibility we share toward all lives awaiting transplants.
If we accept that genetics play a crucial role, then targeted outreach in underrepresented groups becomes not just a charitable act but a medical necessity.
Moreover, emerging technologies like CRISPR editing and stem‑cell derived organs promise a future where genetic mismatches could be engineered away.
However, these breakthroughs also bring ethical dilemmas about where we draw the line between therapy and enhancement.
The cultural narratives around organ donation differ worldwide, and respecting those narratives while promoting equity is a delicate balancing act.
In practice, transplant centers are beginning to incorporate more nuanced HLA typing that goes beyond the classic serological tests.
This richer data can help clinicians predict rejection risk with greater precision, potentially reducing the need for aggressive immunosuppression.
But the data alone won't solve the problem unless policies ensure that all ethnicities have equal access to those advanced diagnostics.
Public health campaigns that demystify donation and highlight stories from diverse donors can shift perceptions in a positive direction.
Ultimately, the intersection of genetics, ethnicity, and organ rejection is a reminder that biology and society are inseparable.
By addressing both the scientific and the social components, we stand a better chance of saving more lives across every community.
Michael Wall
May 7, 2023 AT 02:52It's morally indefensible to overlook genetic matching when lives are at stake.
Christopher Xompero
May 8, 2023 AT 06:39Man, this article tries to sound all scientific but honestly it reads like a textbook copy‑pasted from 2010.
The HLA stuff is important, sure, but the author totally glosses over how hard it is to find a match for folks with rare alleles.
I mean, you can't just say more diverse HLA means more rejection without mentioning the breakthrough of desensitization protocols that are saving patients.
Also, the piece forgets that organ allocation algorithms have been tweaked recently to give minorities a better shot.
Overall, it's a decent overview but missing the latest breakthroughs, and the grammar could use a major overhaul.
Irene Harty
May 9, 2023 AT 10:25One must consider the possibility that the data presented herein is selectively curated to perpetuate existing disparities under the guise of scientific objectivity.
Such omissions are indicative of a broader, orchestrated narrative that benefits the entrenched interests of pharmaceutical conglomerates.
Consequently, the purported "advancements" may serve more as a facade than a genuine effort to promote equitable transplantation outcomes.
Jason Lancer
May 10, 2023 AT 14:12Another typical piece.
Brooks Gregoria
May 11, 2023 AT 17:59Honestly, this whole focus on ethnicity is a distraction from the real issue: the lack of investment in universal immunosuppressive strategies.
Why do we keep beating around the bush with HLA matching when a smarter drug regimen could level the playing field for everyone?
The article pretends that genetics are destiny, but that's a lazy excuse for inadequate research funding.
Stop romanticizing "matching" and start demanding better therapies that work regardless of background.
Only then will we see a true reduction in rejection rates.
Sumit(Sirin) Vadaviya
May 12, 2023 AT 21:45Thank you for shedding light on this nuanced topic. 😊
It is crucial that we continue to invest in both scientific research and community outreach to bridge the gaps identified.
By fostering collaborations across disciplines, we can develop more inclusive protocols that benefit all patients.
I look forward to seeing further developments in personalized transplant strategies.
lindsey tran
May 14, 2023 AT 01:32Wow, this is so awsm!
Seeing science and compassion roll together gives me sooo much hope for the future.
Let's keep pushin the boundaries and make sure everyone gets a fair chance to beat the odds! 💪
Krishna Sirdar
May 15, 2023 AT 05:19It's clear that genetics play a big role, but we also need to think about how we can support patients from all backgrounds.
Education about donation and culturally sensitive counseling can make a real difference.
When communities feel respected and included, they're more likely to participate in donor programs.
becca skyy
May 16, 2023 AT 09:05Totally agree that we need more outreach in diverse neighborhoods.
Seeing real stories from donors really helps break down myths.
Let's keep the conversation going and make transplant access fair for everyone.
Theo Roussel
May 17, 2023 AT 12:52The article aptly highlights the immunogenetic determinants of allograft survival, yet it omits discussion of emerging high-resolution HLA typing platforms.
Incorporating next-generation sequencing for HLA loci can significantly enhance alloantigen prediction models.
Furthermore, integrating pharmacogenomic profiling of tacrolimus metabolism could refine individualized immunosuppressive regimens.
Such multidimensional approaches are essential for reducing acute cellular rejection incidences.
Erick Masese
May 18, 2023 AT 16:39While the exposition is commendably thorough, one must note that a truly nuanced analysis would also address the epigenetic modulation of immune tolerance.
Nevertheless, the prose maintains an engaging cadence, making complex concepts accessible.
Looking forward to more scholarly discourse on this critical subject.
Matthew Charlton
May 19, 2023 AT 20:25Great summary of a challenging topic!
Remember that each step forward-whether it's better HLA matching or improved patient education-adds up to real lives saved.
Encourage your peers to stay informed and to advocate for policies that support equitable transplant access.
By keeping the momentum, we can turn these insights into tangible improvements on the ground.
Stay positive and keep pushing for progress.