Medical Research: Breaking Down New Findings in Drugs and Diseases
If you've ever wondered how medications evolve or why certain diseases behave the way they do, you’re in the right place. Medical research isn't just about labs and complex charts; it’s about real people and better health outcomes. Let's talk about some fresh discoveries that shed light on treatments and conditions you might have heard of.
Amantadine's Expanding Role
Amantadine has been around for a while, mostly known for treating Parkinson's disease and some viral infections like the flu. But recent research is uncovering new reasons to pay attention to this drug. Scientists are exploring its potential beyond what we’ve used it for. There’s promising data about helping brain injury recovery and even managing addiction. Imagine a single medication stepping into entirely new territories—that’s what’s happening with Amantadine right now.
What makes this even more exciting? Research teams are looking closely at how Amantadine affects the brain and nervous system differently depending on the condition being treated. That means future uses might become more personalized, benefiting those who don’t respond well to current standard therapies.
Dopamine’s Crucial Role in Parkinson's and Organ Transplants
Ever hear how dopamine keeps your brain’s messaging smooth? In Parkinson’s disease, dopamine levels drop because the brain cells that produce it die off. This loss leads to the classic tremors and movement troubles. Researchers emphasize that understanding exactly how dopamine loss harms brain function helps in crafting better treatments. New therapies might focus on protecting dopamine-producing cells or even replacing dopamine more effectively.
Switching gears a bit: organ rejection is another area where medical research is making waves. It turns out ethnicity and genetics play a big role in how well a transplanted organ is accepted. Some ethnic groups face more challenges because donors with matching genetics are harder to find. That insight is pushing medical teams to consider genetic factors more closely and to promote donor registrations in diverse communities. The goal? Boosting transplant success rates and saving lives on a broader scale.
Keeping up with medical research might seem overwhelming, but knowing these key developments helps you understand what's possible in healthcare. Whether it’s a drug gaining new uses or genetics shaping treatments, these findings aren't just scientific trivia—they directly impact how diseases get managed and lives get saved.

How Alcohol Consumption Raises Carcinoma Risk: What the Science Says
Explore how alcohol consumption contributes to carcinoma risk, the science behind it, which cancers are most affected, and practical steps to lower your chances.
Linezolid Mechanism of Action: In‑Depth Review of How This Oxazolidinone Stops Bacteria
A detailed look at linezolid’s mechanism, its interaction with bacterial ribosomes, clinical implications, resistance patterns, and how it stacks up against similar drugs.

The Future of Amantadine: New Applications and Research Advances
I recently came across some fascinating research on the future of Amantadine, a medication that has been around for quite some time. It appears that there are new applications and research advances being made that could potentially expand its uses beyond its current scope. From treating Parkinson's disease and influenza to potential roles in brain injury recovery and even addiction management, Amantadine's future looks promising. I can't wait to see how these developments unfold and the possible impact it could have on the medical community. Keep an eye out for updates on this versatile drug!
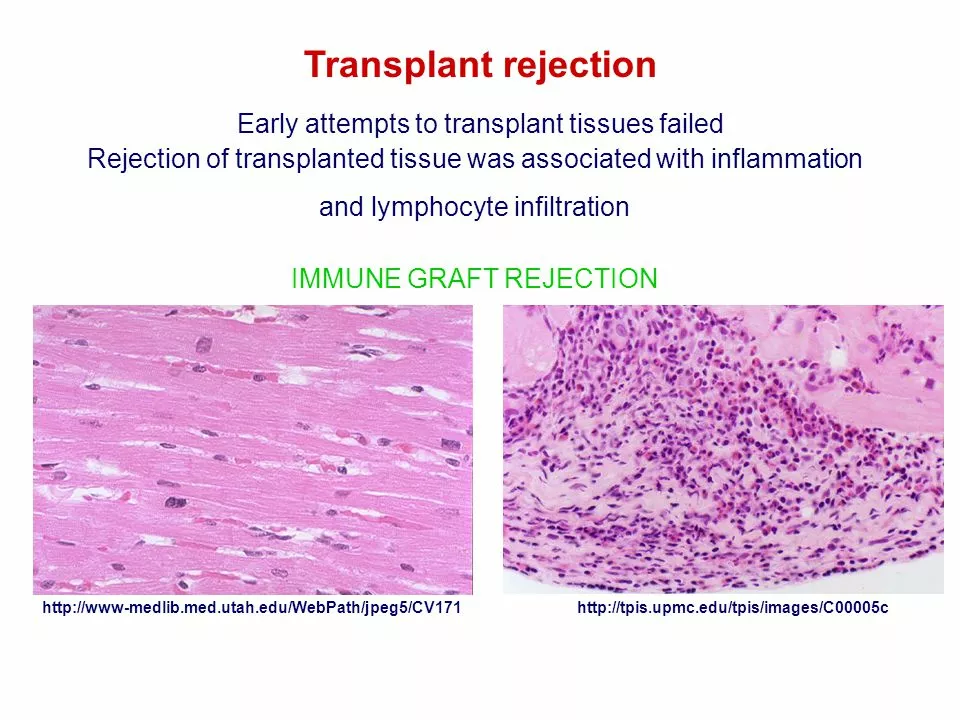
Organ Rejection and Ethnicity: The Impact of Genetic Factors
In my recent research, I've come across the fascinating topic of organ rejection and ethnicity, specifically focusing on the impact of genetic factors. It's intriguing to see how genetic variations among different ethnic groups can affect organ transplant outcomes. For instance, certain populations may experience higher rates of organ rejection due to a lack of well-matched donors within their ethnic group. This highlights the importance of increasing organ donor awareness and participation among diverse populations to ensure the best possible outcomes for all patients in need of transplants. Overall, understanding the role of genetic factors in organ rejection is crucial for improving transplantation success rates and saving more lives.
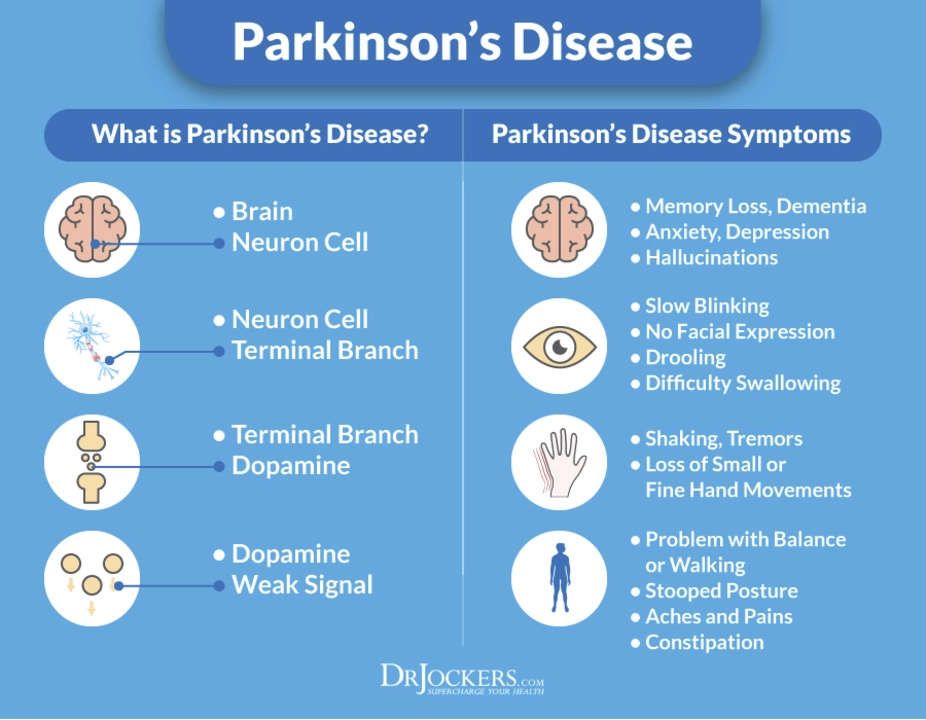
Understanding the Role of Dopamine in Parkinson's Disease
In my recent exploration of Parkinson's Disease, I've discovered the crucial role dopamine plays in this neurological disorder. Dopamine, a vital chemical messenger in our brains, is significantly reduced in Parkinson's patients, leading to issues with movement and coordination. This decrease in dopamine is primarily caused by the death of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. Understanding the role of dopamine in Parkinson's Disease is essential for developing effective treatments and therapies. Further research on this topic may help improve the lives of those affected by this debilitating condition.