Understanding the Impact of Online Pharmacies and Medication Alternatives
Online pharmacies are changing how we get medications. Sites like arlrussia.ru make buying prescription and over-the-counter drugs easier, providing convenience and quick delivery. But with convenience comes responsibility—knowing how to safely buy medicines online is crucial. Articles on InsiderRx cover guides for safely purchasing drugs like Warfarin and Ranitidine, helping you avoid scams and counterfeit products.
Besides online buying, alternatives to popular medications are gaining ground. For instance, in 2025, you'll find new options replacing well-known treatments like Advair Diskus for asthma or Simvastatin for cholesterol management. These alternatives often offer benefits like affordability and fewer side effects. InsiderRx explains these substitutes, so you can make smart choices tailored to your health needs.
Smart Tips for Safe Online Medicine Shopping
When buying medicines online, always look for trusted pharmacies with verified credentials. Check if they require a prescription, protect your data, and offer reliable customer support. Skip deals that look too good to be true—they often signal counterfeit or unsafe products. InsiderRx articles provide step-by-step advice for purchasing critical medications like blood thinners safely, emphasizing legal and medical precautions.
How New Medication Choices Affect Your Health
With more alternatives emerging, you have options that might suit your lifestyle and budget better. For example, newer anticoagulants like Rivaroxaban are changing blood thinning therapy by being safer and more convenient than older drugs. Similarly, for chronic conditions like asthma and COPD, budget-friendly inhaler alternatives let you breathe easier without overspending. Learning about these options equips you to talk confidently with your healthcare provider about what’s best for you.
On top of medications, dietary supplements like hops and goji berries are gaining popularity for their health benefits, such as stress relief and immune support. Understanding how these fit into your health routine adds another layer to managing well-being naturally alongside traditional treatments.
By staying informed about online pharmacies, medication alternatives, and health supplements, you can navigate healthcare options more safely and effectively. InsiderRx offers practical, user-friendly guidance to help you get the best results with your medicines and treatments without the usual confusion and risks.

The Impact of Erosive Esophagitis on Mental Health
Erosive esophagitis is a condition that has been weighing on my mind lately, as it not only affects a person's physical health but also has significant impacts on mental health. The constant pain and discomfort caused by this inflammation can lead to increased stress and anxiety, which in turn, exacerbates the condition. Moreover, the disruption to daily activities and the need to follow strict dietary restrictions can result in feelings of isolation and depression. It's crucial that we acknowledge the connection between erosive esophagitis and mental health, and seek appropriate treatment and support for both aspects. By addressing these concerns holistically, we can improve the overall well-being of those affected by this condition.
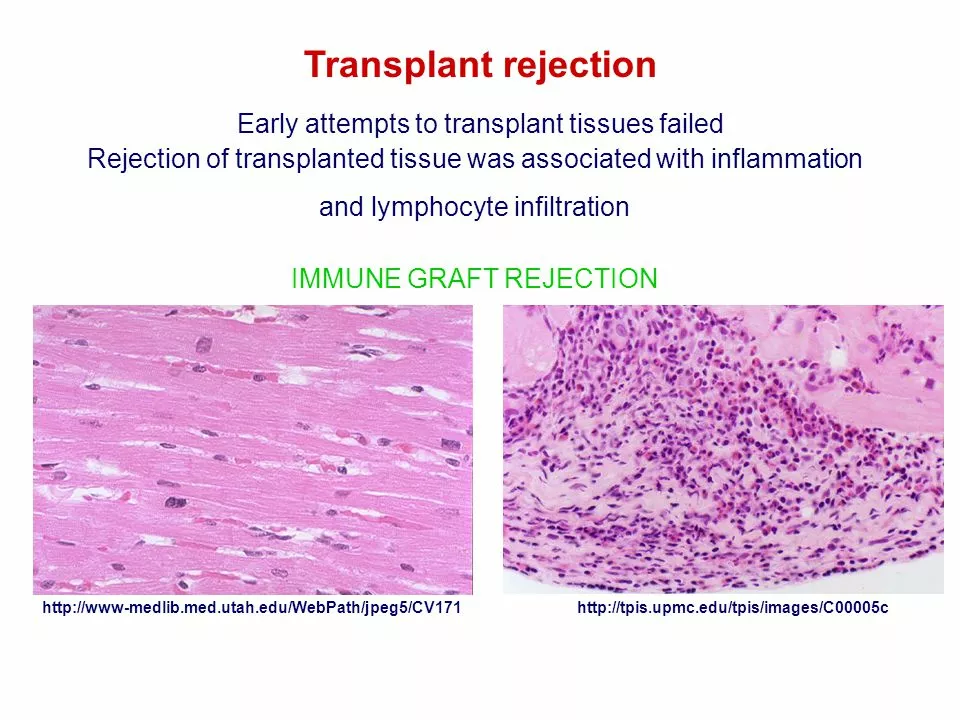
Organ Rejection and Ethnicity: The Impact of Genetic Factors
In my recent research, I've come across the fascinating topic of organ rejection and ethnicity, specifically focusing on the impact of genetic factors. It's intriguing to see how genetic variations among different ethnic groups can affect organ transplant outcomes. For instance, certain populations may experience higher rates of organ rejection due to a lack of well-matched donors within their ethnic group. This highlights the importance of increasing organ donor awareness and participation among diverse populations to ensure the best possible outcomes for all patients in need of transplants. Overall, understanding the role of genetic factors in organ rejection is crucial for improving transplantation success rates and saving more lives.