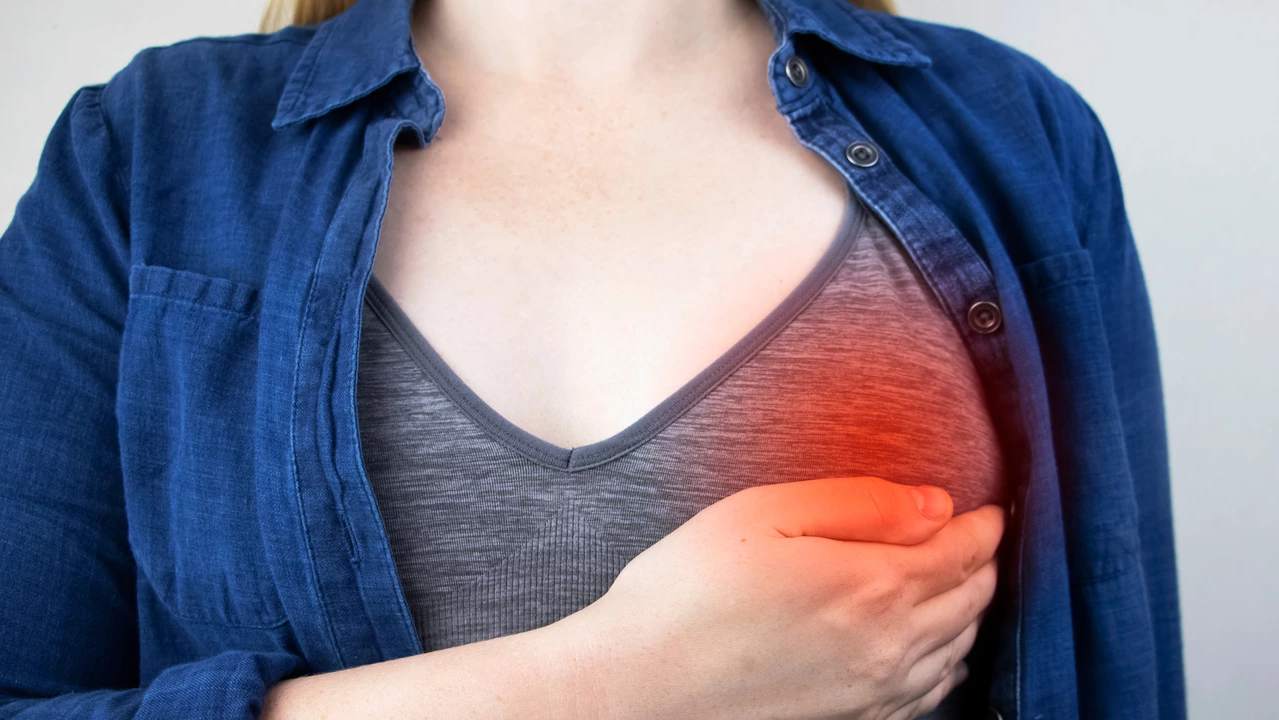
Mastitis: What You Need to Know About This Common Breast Infection
Mastitis usually pops up when a bacteria gets into the breast tissue, often during breastfeeding. It causes painful swelling, redness, and sometimes a fever. Recognizing it early is key to stopping it from getting worse because untreated mastitis can lead to an abscess, a painful pocket of pus that requires medical care.
One of the main culprits is milk getting trapped in the breast, creating an environment where bacteria love to grow. This can happen if the baby isn’t latching properly or if feeding sessions are skipped. Sometimes cracked nipples or clogged milk ducts let bacteria in, making infection more likely.
How to Spot Mastitis Symptoms Fast
Signs usually hit quickly: you’ll notice breast pain, warmth, and swelling. The skin might look red and feel tender to touch. If you have a fever and feel rundown alongside these symptoms, it's a strong sign of infection. Don’t ignore these signs or push through the pain because the infection can get worse or spread.
Practical Ways to Treat and Prevent Mastitis
Treatment usually involves antibiotics to knock out the infection and pain relievers to tackle discomfort. Keeping the milk flowing is super important, so frequent feeding or pumping helps clear clogged ducts. Applying warm compresses and resting can ease pain and swelling too.
Prevention is all about good breastfeeding habits—make sure the baby is latching well and feed often enough to avoid milk buildup. If issues like cracks or blocked ducts appear, treating them early cuts down the risk of mastitis. Staying hydrated and maintaining breast hygiene also helps keep infections at bay.
If you feel symptoms are severe or don’t improve in a couple of days, chatting with your healthcare provider is a must. They can check if a more serious problem like an abscess needs special care.
Dealing with mastitis can be painful, but with quick action and proper care, recovery is usually smooth. Remember, you’re not alone—many face this and managing it well lets you get back to enjoying those precious bonding moments stress-free.
The use of clavulanate in treating mastitis and other breast infections
As a blogger, I recently came across the use of clavulanate in treating mastitis and other breast infections. Clavulanate is a powerful compound that when combined with antibiotics, can effectively combat bacteria resistant to traditional treatments. In the case of mastitis, which is a painful inflammation of breast tissue, using clavulanate has shown promising results. This is especially important for nursing mothers, as it helps to reduce pain and prevent further complications. Overall, incorporating clavulanate into the treatment of breast infections could significantly improve patient outcomes.